8. Cross Product (aka Vector Product) of 2 Vectors
Suppose we have 2 vectors A and B. These 2 vectors lie on a plane and the unit vector n is normal (at right angles) to that plane.
The cross product (also known as the vector product) of A and B is given by:
A × B = |A| |B| sin θ n
The right hand side represents a vector at right angles to the plane containing vectors A and B.
Note: Some textbooks use the following notation for the cross product: A∧B.
Example
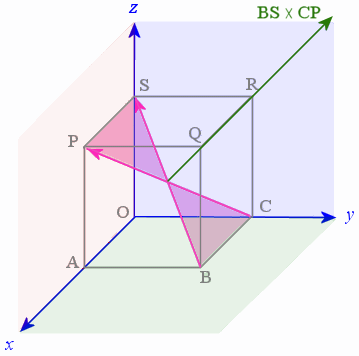
In the earlier application involving a cubic box (see Vectors in 3D Application), we had a unit cube that had one corner at the origin. We found that the diagonal vectors BS and CP meet at an angle of `70.5^@` at the center of the cube.
Using the same unit cube, find the vector product of the vectors BS and CP.
Answer
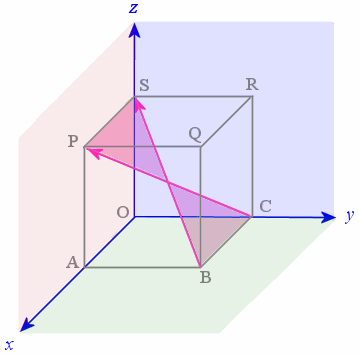
Using the formula
A × B = |A| |B| sin θ n
and our values from before which were
|BS| = √3
|CP| = √3
θ = 70.5°
we have:
|BS| × |CP| |
= |BS| |CP| sin θ n = (√3)(√3) sin 70.5° n = 2.828 n |
This means our result is a vector with magnitude `2.828` units and direction perpendicular to the plane containing BS and CP, indicated in green in the following diagram.